What You’ll Learn and Why It Matters
You’ll learn how to tell the difference between rule-based automation and agentic AI—and, more importantly, how to choose the right one for a real business workflow. Automation excels at predictable, repetitive tasks. Agentic AI shines when you need adaptable judgment, multi-step planning, and tool use guided by goals. Use this guide to move faster, reduce rework, and scale safely without guesswork.
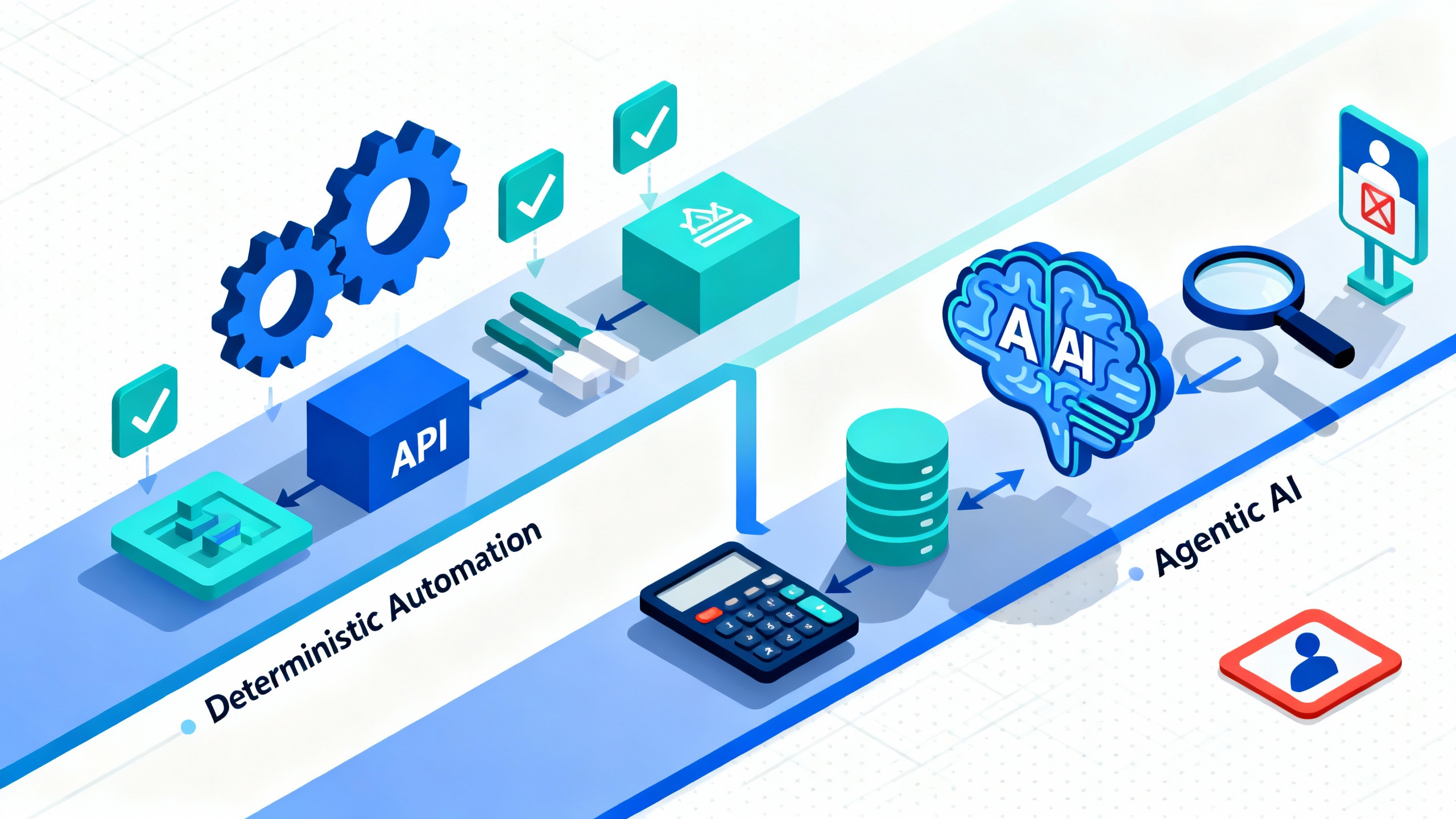
Automation vs Agentic AI at a glance
| Dimension | Classic Automation | Agentic AI |
|---|---|---|
| Core behavior | Executes predefined rules and flows | Plans toward a goal, decides next actions, calls tools |
| Inputs | Structured, stable | Mixed/ambiguous, natural language |
| Change tolerance | Low (requires reprogramming) | Higher (adapts with prompts/tools) |
| Typical stack | RPA, iPaaS, BPM | LLMs + tool use, planners, memory, retrieval |
| Strengths | Speed, reliability, compliance | Flexibility, reasoning, handling edge cases |
| Risks | Brittle with edge cases | Hallucinations, oversight, cost variability |
| Best for | Deterministic tasks at scale | Judgment-heavy or evolving tasks |
- References: Gartner on Hyperautomation, NIST AI Risk Management Framework, LangChain Agents, OpenAI Tool Use, Anthropic Tool Use
Preparation
- Pick one workflow with measurable pain (e.g., slow cycle time, high rework).
- Gather 10–50 recent, representative examples (inputs, outputs, edge cases).
- Define success metrics: cycle time, error rate, human override rate, cost per action.
- Confirm data access and permissions; identify any PII or regulated data.
- Nominate an accountable owner and a reviewer for human-in-the-loop checks.
1. Clarify Outcomes and Decision Types
- Write a one-sentence goal: “Reduce ticket triage time from 2h to 10m with <2% misroutes.”
- Classify the core decision: deterministic (clear rules), bounded judgment (some interpretation), or open-ended (creative/strategic).
- Set risk tolerance: What’s the maximum acceptable error, and which errors are intolerable?
Examples:
- Invoice field extraction → deterministic. Good for RPA/templated OCR.
- Customer email drafting → bounded judgment. Candidate for agentic AI with approval.
- Root-cause analysis from logs → open-ended. Agentic AI with strong guardrails.
2. Decompose the Workflow and Tag Each Step
- Break the process into 5–12 steps (swimlane style): inputs → transforms → decisions → outputs.
- Tag each step: D (deterministic), B (bounded judgment), O (open-ended).
- Note dependencies and integration points (CRM, ERP, ticketing, knowledge base).
Actionable split:
- D: Use classic automation (iPaaS/BPM/RPA). Keep it fast and explicit.
- B: Use agentic components but require human approval or validation rules.
- O: Use agentic AI with tool use and sandboxed execution; log everything.
TipKeep agents on the smallest surface area
Constrain agents to only the steps that truly need judgment. Everything else: deterministic automation.
3. Design the Minimum Viable Flow (with Guardrails)
- Draft a hybrid flow: automation handles orchestration; agent(s) handle judgment steps.
- For each agent step, list allowed tools (search, DB query, calculator, ticket API) and banned actions.
- Specify validation gates: schema checks, policy filters, and human approvals.
- Write prompts with structure: role, goal, constraints, tools, examples, and output schema.
Example guardrails:
- Deterministic pre- and post-validators (regex, JSON schema, policy rules).
- Human gate for high-risk outputs (e.g., regulatory language, refunds > $200).
- Automatic fallback to deterministic baseline if confidence is low or tools fail.
4. Choose the Right Tools for Each Piece
- Deterministic orchestration: iPaaS (Zapier, Make), BPM (Camunda), or workflow engines (Temporal, Airflow).
- Task automation: RPA (UiPath, Automation Anywhere) when dealing with legacy UIs.
- Agentic stack: LLM provider (OpenAI, Anthropic, etc.) + agent framework (LangChain Agents/LangGraph, Microsoft Autogen) + retrieval (vector DB) + tool connectors.
- Compliance: PII redaction, secrets management (Vault), audit logging.
Selection quick-check:
- If it’s clicks and forms → RPA.
- If it’s APIs and simple logic → iPaaS/BPM.
- If it’s messy language or multi-hop reasoning → agentic with tool use.
- If it’s regulated or high-risk → add human-in-the-loop and policy checks (see NIST AI RMF and ISO/IEC 42001).
5. Implement Control Loops, Monitoring, and Evals
- Log inputs, prompts, tool calls, outputs, approvals, and errors with trace IDs.
- Create a small gold test set (20–50 examples) to run on every change.
- Add automated checks: schema validation, PII filters, profanity/policy screens, numeric sanity rules.
- Track metrics per step: accuracy, latency, cost, and override rate.
- Establish stop-loss rules: auto-disable agent if override rate > threshold.
Helpful references: OpenAI Function/Tool Use, Anthropic Tool Use, LangChain Agents.
6. Pilot, Measure, and Iterate
- Run the hybrid flow on a small slice (5–10% of volume) for 2–4 weeks.
- Compare against baseline automation: cycle time, accuracy, cost per action, and human time saved.
- Iterate prompts, tools, and validators weekly. Reduce human gates only when data supports it.
- Document learnings: where agents help, where rules beat AI, and where the process needs simplification.
7. Productionize with Governance and Safety Nets
- Permissions: least privilege for tools and data; rotate keys; segregate duties.
- Observability: dashboards for success/override rates, latency, cost, drift alerts.
- Change management: version prompts and workflows; require reviews for risky changes.
- Compliance: map risks using NIST AI RMF functions (Govern, Map, Measure, Manage) and align with ISO/IEC 42001 where applicable.
- Continuous evaluation: quarterly audits, red-team tests, and policy updates.
Pro Tips and Common Mistakes
- Start with automation, then add agents where rules fail or maintenance is crushing.
- Prefer tool-using agents over “pure text” reasoning; tools increase reliability and verifiability.
- Keep outputs structured (JSON/fields) so validators can catch errors.
- Cache and reuse intermediate results to reduce cost and latency.
- Don’t mix too many tools early; each integration adds failure modes.
- Avoid silent failures. Every agentic decision should be observable and explainable at audit time.
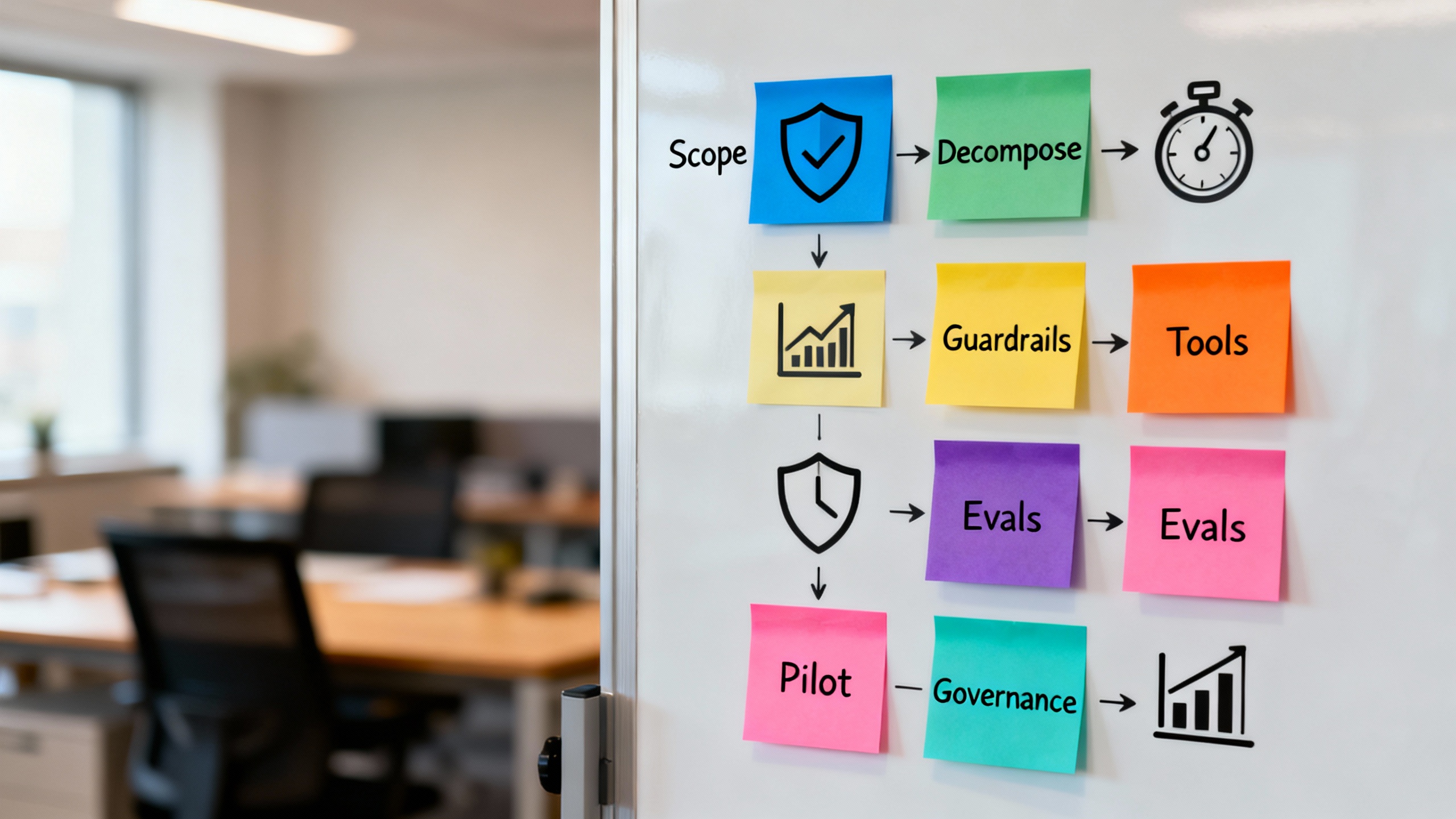

Conclusion
Automation and agentic AI aren’t rivals—they’re teammates. Use automation for the backbone: speed, consistency, and compliance. Drop in agentic components only where judgment and adaptability create measurable value, and box them in with tools, tests, and approvals. Start with a narrow pilot, measure hard, and scale what actually works.
Further reading: Gartner Hyperautomation Overview, McKinsey on Generative AI Productivity, NIST AI RMF.